Anesthesiologists play a vital role in healthcare. They use a range of tools to ensure patient safety and comfort during procedures. From syringes to advanced monitoring systems, these tools are essential for precise care. In places like Great Neck, NY pain management has advanced thanks to these innovations. Let’s explore the key instruments anesthesiologists rely on in their work.
Syringes and Needles
The syringe and needle might seem simple, but they are the workhorses in anesthesia. They allow for the precise delivery of medications. Different sizes cater to various needs, ensuring accuracy in dosages. Syringes also come in disposable forms for hygiene and safety.
Anesthesia Machines
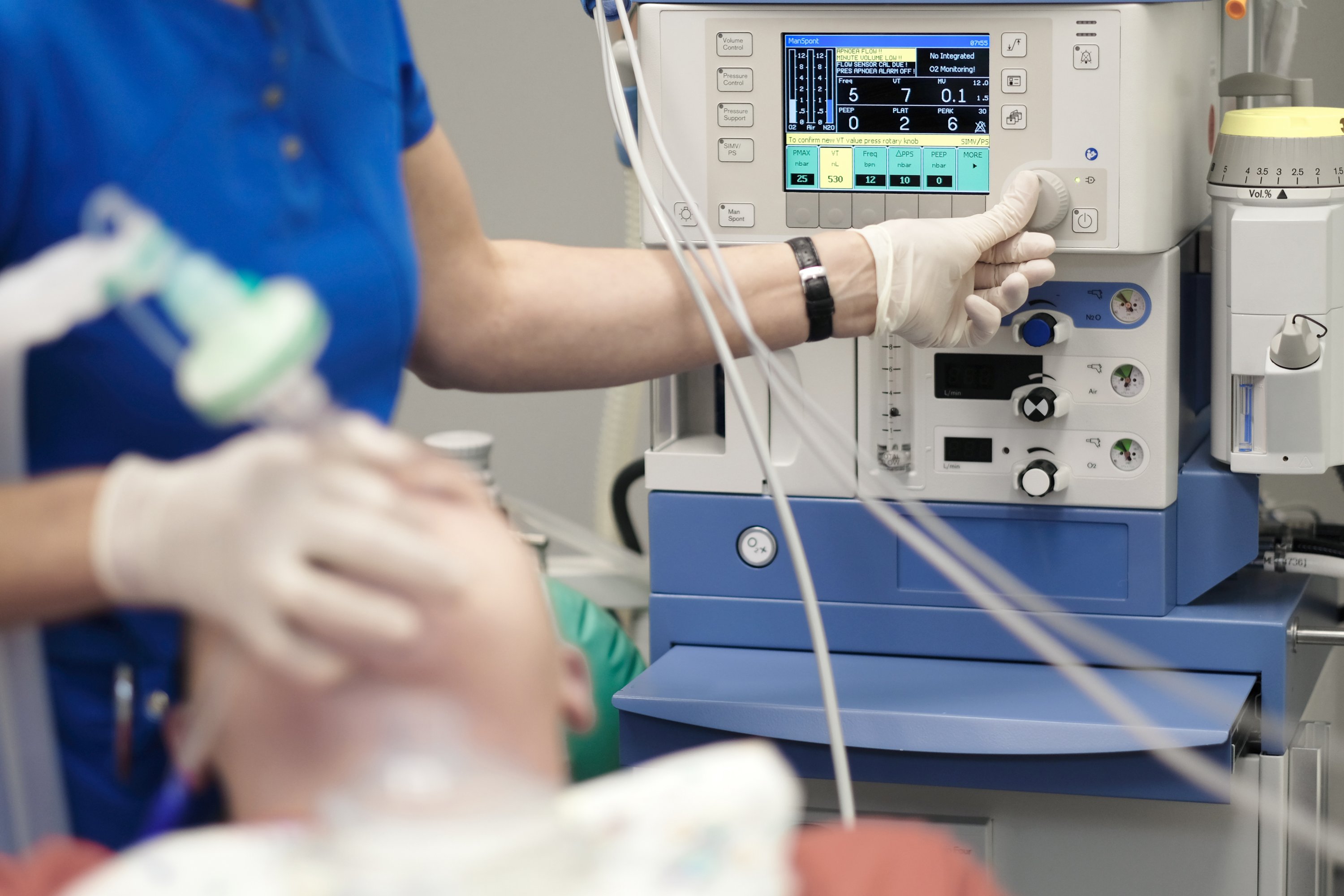
Anesthesia machines are complex, yet crucial. They deliver a mixture of gases to keep a patient unconscious and pain-free during surgery. These machines monitor and control the amount of gas, adapting to the patient’s needs. According to the FDA, modern machines also include safety features to detect issues early.
Monitoring Equipment
Keeping a close watch on vital signs is essential. Anesthesiologists use monitors to track heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. These devices alert the team to any changes in a patient’s condition. Continuous monitoring means quick responses to ensure safety.
Endotracheal Tubes
In many surgeries, patients need help with breathing. Endotracheal tubes are inserted into the airway to deliver oxygen and anesthesia. These tubes come in different sizes to fit various patients, from children to adults.
Laryngoscopes
Laryngoscopes help anesthesiologists place endotracheal tubes accurately. They provide a clear view of the throat, making the process smoother. This tool ensures that the tube is in the right place, avoiding complications.
Comparing Tools
Let’s take a look at a comparison of some key tools used by anesthesiologists:
| Tool | Purpose | Additional Info |
| Syringe and Needle | Medication delivery | Various sizes available |
| Anesthesia Machine | Gas delivery | Includes safety features |
| Monitor | Vital sign tracking | Continuous updates |
| Endotracheal Tube | Airway management | Different sizes |
| Laryngoscope | Tube placement | Clear view of throat |
Regional Anesthesia Tools
When full anesthesia isn’t needed, regional approaches are used. Nerve blocks are one example, requiring specific needles and ultrasound machines. These tools help in targeting precise areas and reducing pain without full sedation. The NIH highlights the benefits of such targeted methods.
Training and Expertise
Anesthesiologists undergo extensive training. They learn to use these tools effectively, ensuring the best outcomes for patients. Mastery of these instruments is critical in their role. This expertise allows them to adapt to different situations and patient needs with confidence.
Conclusion
Anesthesiologists have a critical job that hinges on expert use of specialized tools. From the basic syringe to complex machines, each tool plays its part. Their work is indispensable in modern medicine, ensuring safety and comfort during surgical procedures. The tools they use reflect their commitment to excellence and patient care.